What Is The HDG Process?
Learn More About Our Hot-Dip
Galvanising Process
What Is HDG Process?
The hot-dip galvanising (HDG) process encompasses three fundamental stages:

Our Process
North West Galvanising provides bespoke galvanising services, protecting metal products from corrosion and prolonging their lifespan. Our galvanising process involves several meticulous steps for optimal results — take a closer look at how we carry out hot-dip galvanising
Galvanising
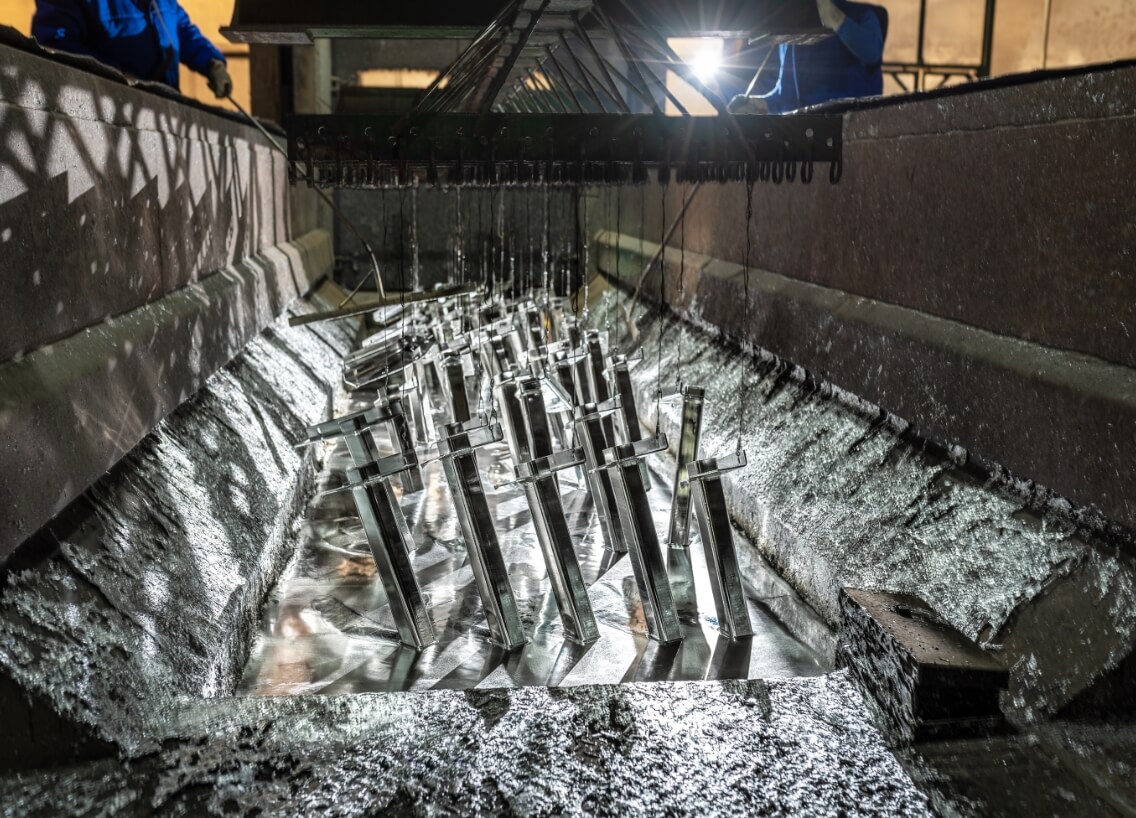
At the galvanising stage of the process, the material undergoes a remarkable transformation when immersed in a bath containing molten zinc. It must adhere to international specifications, which mandate at least 98% zinc purity with temperatures ranging between 815-850°F (435-455°C).
Inside an atmospheric kettle lies an amazing metamorphosis: zinc from the bath engages in an extraordinary chemical reaction with iron present in steel, producing zinc-iron alloy layers that form strong metallurgical bonds with steel resulting in robust and long-term coatings that resist impact and corrosion. These intermetallic layers typically receive additional protection with a protective outer coating of pure zinc to withstand impacts and improve corrosion resistance.

Once the galvanised items have achieved the desired coating growth, they are carefully removed from their galvanising bath, and excess zinc is carefully removed through draining. Although no longer submerged in the bath, metallurgical reactions still occur due to proximity to its elevated temperatures; for cooling purposes, these galvanised articles may either be immersed in a passivation solution or water, or left outside until ambient temperatures can be reached gradually.
Galvanising is an intriguing interplay between steel, molten zinc and the galvanising bath that forms its core. Galvanised items from this process provide exceptional corrosion protection and lasting defence against time and environmental elements.
Inspection
Inspection of hot-dip galvanised steel is a straightforward and expeditious process. Inspection will focus on two essential properties of the galvanised coating: its thickness, and its overall appearance and surface condition. Various physical tests can be conducted to assess these aspects, providing invaluable insights into its thickness, uniformity, adhesion and visual appeal.
Galvanised products adhere to stringent, industry-wide standards. ISO 1461 is the British standard for hot-dip galvanised coatings on iron and steel articles in the UK and Ireland.
It specifies the general properties of coatings and test methods for coatings applied by dipping steel articles.
This comprehensive standard covers various facets of galvanising processes to ensure consistency and quality across the industry — for instance, minimum coating thickness requirements across product categories and specifications regarding zinc metal composition used during galvanising processes.
Adherence to this stringent standard assures customers and industry professionals that galvanised steel fulfils defined performance and quality criteria, providing a reliable framework to assess its longevity and inspiring confidence in its ability to provide excellent corrosion protection and aesthetic appeal.